Radio Astronomy Units Conversion
The Radio Astronomy Units table
(PDF file or Excel XLSX file)
shows dBm, Watts, Volts across 50 ohms, temperature in K/1Hz, dBW and Jansky equivalent values.
This is the first step to convert the Tektronix MDO4104-6 spectrum analyzer data in dBm measurements to other radio astronomy units.
Conversion formulas:
- Power in
dBm
is the vertical scale of the spectrum trace measured by the spectrum analyzer.
- Watts
- Watts = POWER(10,dBm/10 -3).
- 0 dBm = 0.001 Watts or 1 mW.
- -10 dBm = 0.0001 Watts or 0.1 mW.
- -60 dBm = 0.000001 Watts or 1 uW.
- Volt (usually in uV) across 50
ohms is used for receiver measurements.
- Volts across 50 ohms = SQRT(Watts*50).
- -106 dBm = 1.1 uV across 50 ohms
- Noise temperature in
Kelvin.
- Noise temperature in Kelvin = Watts/1.38E-23/1Hz.
- 1.8E+9 K = 25.1E-15 W/1.38E-23/1 Hz.
- Noise temperature is in per bandwidth of 1Hz.
- dBW
- dBW = 10*LOG(Watts,10) or dBm-30.
- 0 dBW = 1 Watt = 30 dBm.
- -106 dBm = -136 dBW = 25.1E-15 Watts
- Jansky
(named in honor of
Karl G. Jansky,
founder of radio astronomy,
Electrical Disturbances Apparently of Extraterrestrial Origin).
- Jy = =POWER(10,(dBW+260)/10)
- 1 Jy = -260 dBW/1m^2/1Hz = 10E-26 Watts/1m^2/1Hz.
- -106 dBm = 2.5E+12 Jy/1m^2/1Hz.
- Jy is in per
meter
squared and per bandwidth in Hz.
- Used in Figure 1.6 Jovian flux density as a function of frequency for both Io-related and non-Io-related emissions, in Listening to Jupiter, A Guide for the Amateur Radio Astronomer, Second Edition, by Richard S. Flagg, page 1-6.
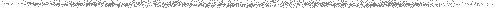
Radio Astronomy Units Table Page 3

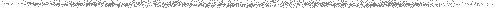
Radio Astronomy Units Table Page 4

© 1998-2014 David Haworth
![]()
![]()

